Introduction
In vitro generation of perfusable 3D microvessels is an important goal for tissue engineering and reliable modeling of blood vessel function. In vitro blood vessel models have yet to accurately reproduce the dynamics and responses of endothelial cells in order to grow perfusable and functional 3D vascular networks.
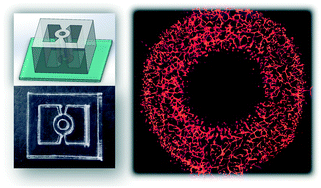
In this paper, the author talks about different vascularization mechanisms including vasculogenesis and angiogenesis to create a microfluidic device for a 3D vascularized organ-on-a-chip, 3D perfusable microvasculature inside a tissue chamber with various shapes under different microenvironment factors. Read the paper below to learn more.
How to culture vascularized & immunocompetent 3D models in a standard Multiwell
Abstract
The author states that “Reconstruction of 3D vascularized microtissues within microfabricated devices has rapidly developed in biomedical engineering, which can better mimic the tissue microphysiological function and accurately model human diseases in vitro.
However, the traditional PDMS-based microfluidic devices suffer from the microfabrication with complex processes and usage limitations of either material properties or microstructure design, which drive the demand for easy processing and more accessible devices with a user-friendly interface. Here, we present an open microfluidic device through a rapid prototyping method by laser cutting in a cost-effective manner with high flexibility and compatibility.
This device allows highly efficient and robust hydrogel patterning under a liquid guiding rail by spontaneous capillary action without the need for surface treatment. Different vascularization mechanisms including vasculogenesis and angiogenesis were performed to construct a 3D perfusable microvasculature inside a tissue chamber with various shapes under different microenvironment factors.
Furthermore, as a proof-of-concept, we have created a vascularized spheroid by placing a monoculture spheroid into the central through-hole of this device, which formed angiogenesis between the spheroid and microvascular network.
This open microfluidic device has great potential for mass customization without the need for complex microfabrication equipment in the cleanroom, which can facilitate studies requiring high-throughput and high-content screening.”
References
Li Q, Niu K, Wang D, Xuan L, Wang X. Low-cost rapid prototyping and assembly of an open microfluidic device for a 3D vascularized organ-on-a-chip. Lab Chip. 2021 Sep 28. doi: 10.1039/d1lc00767j. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34581377.
FAQ
An important goal for tissue engineering is the in vitro generation of 3D microvessels that can be perfused with fluid. Blood vessel models created in a laboratory setting have not yet been able to accurately reproduce the dynamics of endothelial cells. The responses of these cells are also not well copied. These factors are necessary to grow functional 3D vascular networks that allow fluid to pass through them. The presented paper discusses different mechanisms for forming blood vessels. These mechanisms include vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. They are used as a basis to create a microfluidic device. This device is intended for a 3D organ-on-a-chip model containing its own blood vessels. The aim is to create a 3D perfusable microvasculature inside a tissue chamber.
The reconstruction of 3D vascularized microtissues within microfabricated devices has developed at a fast pace in biomedical engineering. Such models can better reproduce tissue microphysiological function and accurately model human diseases in vitro. However, traditional devices that are PDMS-based suffer from several problems. Their microfabrication involves complex processes. They also have usage limitations related to either their material properties or their microstructure design. This situation has created a demand for devices that are easier to process. More accessible devices that are simple to use are also needed.
An open microfluidic device is presented. It is produced through a rapid prototyping method using laser cutting. This approach is low-cost and provides high adaptability and the ability to work with other systems. The device allows for dependable hydrogel patterning under a liquid guiding rail. This is achieved by capillary action that occurs on its own, which means no surface treatment is needed. This device has a capability for mass customization. It does not require the use of complex microfabrication equipment in a cleanroom. This can assist studies that require high-volume and detailed screening.
Different mechanisms for blood vessel formation, including vasculogenesis and angiogenesis, were performed. This was done to construct a 3D perfusable microvasculature. This network was built inside a tissue chamber, which could have different shapes, and was tested under different local conditions. As a demonstration of its use, a vascularized spheroid was created. A monoculture spheroid was placed into a central through-hole in the device. Following this, angiogenesis, which is the formation of new blood vessels, was observed between the spheroid and the microvascular network.