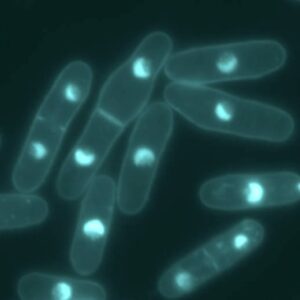
Yeast cells strains expressing a GFP labeled exocyst complex component were grown overnight in standard yeast peptone dextrose medium (YPD) and were cultured at 30°C with continuous shaking at 280 rpm. After overnight culture, cells were washed 3x with H2O and diluted 10-fold in SC-All media for 2h at 30°C. Afterwards cells were mounted on glass cover slips coated with Concanavalin A.
An iMIC-based microscopy (Thermo/Till Photonics) with an Olympus x100 1.45 NA objective was used for image acquisition.
Images were taken with Andor iXON DU-897 EMCCD using the LiveAcquisition software (Thermo).
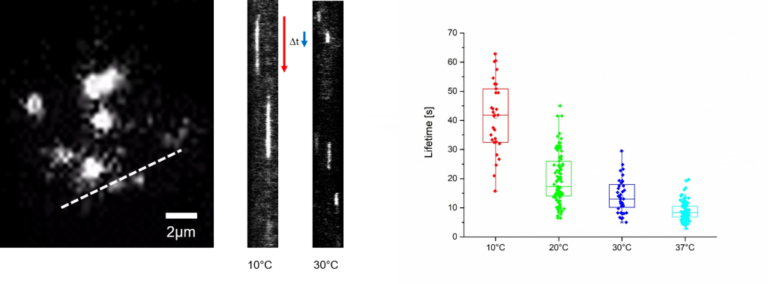
Shifts between temperatures were performed using the CherryTemp device with a 1 min delay to allow for cell adaption.
Ultra fast temperature shift device for in vitro experiments under microscopy
Recorded timelapses of exocytosis were analyzed via kymographs to determine the lifetimes of exocytic events at different temperatures.