Introduction
In this application note, we show the comparision between blocking fission yeast cdc25-22ts mutants in a thermalized waterbath vs. blocking them on a microscope slide using CherryTemp.
Experimental conditions
Application example: Block and release of cdc25-22 S. pombe ts mutants.
For the flask experiment, fission yeast cdc25-22cells were blocked at the G2/M transition by placing a flask for 4 hours in a waterbathat restrictive temperature (36.5 °C). Synchronous release into the cell cycle was achieved by a quick immersion of the flask on ice-cold water until 25°C was reached (temperature measured by inserting a thermometer in the flask). Cells were then placed on a microscope slide and were imaged for septation index scoring.
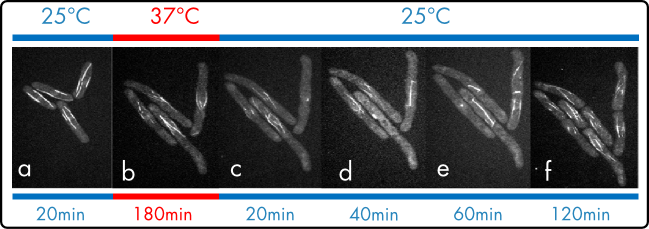
For the CherryTemp experiment, asynchronously growing fission yeast cdc25-22 cells were placed on a CherryTemp mounted system. Cells were blocked at the G2/M transition for 4 hours at restrictive temperature (36.5 °C). Synchronous release into the cell cycle was achieved by a quick shift (10 seconds) into permissive temperature (25°C).
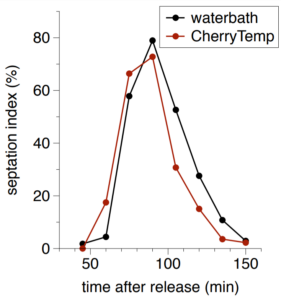
Septation index is an indicator of the progression of fission yeast cells into the cell cycle.Septation index in both experiments shows a high synchrony in the release. Synchrony and time of releasewith both methods are very similar.
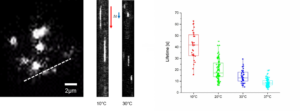
High synchrony was obtained as well when blocking nda3-KM311 mutants at 16°C with CherryTemp and measuring septation index upon release to 32°C.
Ultra fast temperature shift device for in vitro experiments under microscopy
For the flask experiment, fission yeast cdc25-22cells were blocked at the G2/M transition by placing a flask for 4 hours in a waterbathat restrictive temperature (36.5 °C). Synchronous release into the cell cycle was achieved by a quick immersion of the flask on ice-cold water until 25°C was reached (temperature measured by inserting a thermometer in the flask). Cells were then placed on a microscope slide and were imaged for septation index scoring.
For theCherryTempexperiment, asynchronously growing fission yeast cdc25-22 cells were placed on a CherryTemp mounted system. Cells were blocked at the G2/M transition for 4 hours at restrictive temperature (36.5 °C). Synchronous release into the cell cycle was achieved by a quick shift (10 seconds) into permissive temperature (25°C).
Septation index is an indicator of the progression of fission yeast cells into the cell cycle.Septation index in both experiments shows a high synchrony in the release. Synchrony and time of releasewith both methods are very similar.
High synchrony was obtained as well when blocking nda3-KM311 mutants at 16°C with CherryTemp and measuring septation index upon release to 32°C.