SCIENTIFIC POSTER DOWLOAD —
Skin sensitization and safety assessment based on an in vitro 3D vascularized fully differentiated immunocompetent skin model
Fassini D, Mejri H, Fernandes P, Simon M, Homs Corbera A, Poinsot C, Gaudriault P, Filaire E
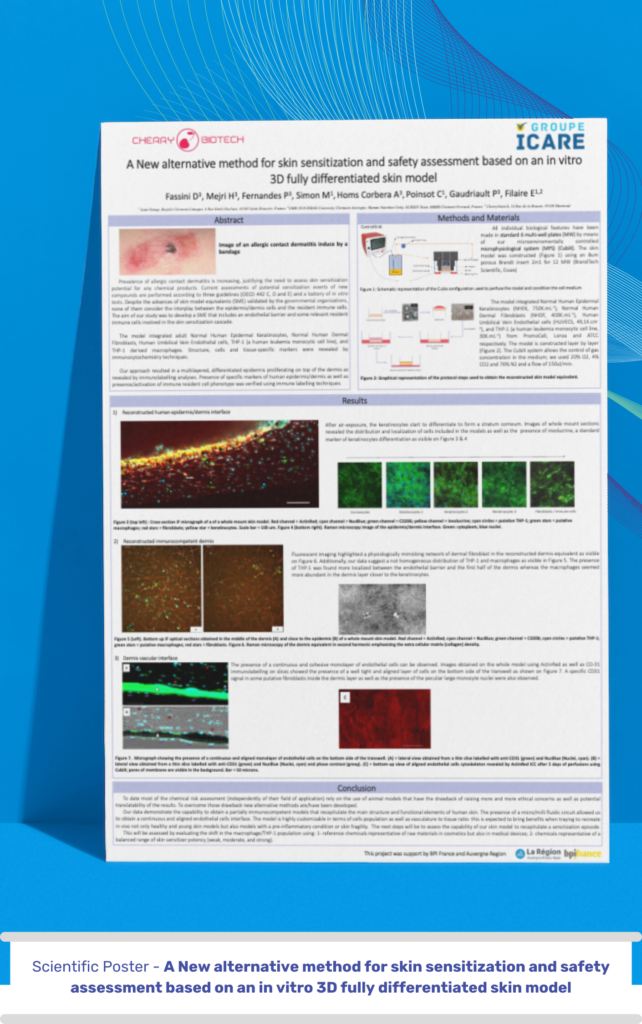
With the rising prevalence of allergic contact dermatitis, accurately assessing the skin sensitization potential of chemical products is increasingly critical. Current methods, guided by three OECD guidelines and a set of in vitro tests, have advanced with skin model equivalents (SMEs). However, these models lack the crucial interaction between epidermis/dermis cells and resident immune cells, a key factor in skin sensitization.
Our study aimed to develop an SME that encompasses an endothelial barrier and relevant resident immune cells, enhancing the understanding of skin sensitization processes. We integrated adult Normal Human Epidermal Keratinocytes, Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts, Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells, THP-1 cells, and THP-1 derived macrophages into our model.
This innovative approach led to a multi-layered, differentiated epidermis that proliferates atop the dermis, as confirmed by immunolabelling analyses. Our model also successfully verified the presence and activation of specific human epidermis/dermis markers and resident immune cell phenotypes, offering a more comprehensive method for skin sensitization and safety assessment.
The poster, title: A New alternative method for skin sensitization and safety assessment based on an in vitro 3D fully differentiated skin model – is free to download here. Don’t miss out!