Introduction
Microphysiological systems may predict drug pharmacokinetics, effectiveness and toxicity more accurately in humans. Pharmacokinetics-On-a-Chip: In Vitro Microphysiological Models are the future of emulating of Drugs ADME, this new technology has considerable promise as a tool for re-creating important physiological characteristics in humans and for developing in vitro approaches for forecasting effects on the physiology.
Pharmacokinetics-On-a-Chip have been shown to be effective in modeling important drug bioavailability mechanisms, with an emphasis on drug metabolism. They believe that organ-on-chip technology may be utilized to build innovative tests to model and predict important physiological responses involved in medication bioavailability, effectiveness, and toxicity.
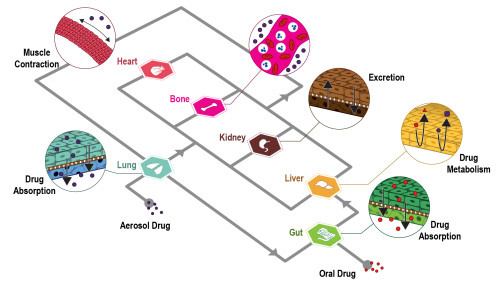
Microphysiological systems might be beneficial for supporting and accelerating efforts in rare illnesses, stratified medicine, and nanomedicine, sectors that are garnering industry and public attention, in addition to enhancing research and development efficiency in general.
How to culture vascularized & immunocompetent 3D models in a standard Multiwell
Abstract of Pharmacokinetics-On-a-Chip: In Vitro Microphysiological Models for Emulating of Drugs ADME
The authors state that “Despite many ongoing efforts across the full spectrum of pharmaceutical and biotech industries, drug development is still a costly undertaking that involves a high risk of failure during clinical trials. Animal models played vital roles in understanding the mechanism of human diseases.
However, the use of these models has been a subject of heated debate, particularly due to ethical matters and the inevitable pathophysiological differences between animals and humans. Current in vitro models lack the sufficient functionality and predictivity of human pharmacokinetics and toxicity, therefore, are not capable to fully replace animal models.
The recent development of micro-physiological systems has shown great potential as indispensable tools for recapitulating key physiological parameters of humans and providing in vitro methods for predicting the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in humans.
Integration of Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME) processes within one close in vitro system is a paramount development that would meet important unmet pharmaceutical industry needs. In this review paper, synthesis of the ADME-centered organ-on-a-chip technology is systemically presented from what is achieved to what needs to be done, emphasizing the requirements of in vitro models that meet industrial needs in terms of the structure and functions.”
References
Ramadan Q, Fardous RS, Hazaymeh R, Alshmmari S, Zourob M. Pharmacokinetics-On-a-Chip: In Vitro Microphysiological Models for Emulating of Drugs ADME. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2021 Jul 29:e2100775. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202100775. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34323392.
FAQ
"Pharmacokinetics-On-a-Chip" models are engineered in vitro systems. They are being developed to copy human physiological characteristics. These systems may predict drug pharmacokinetics, effectiveness, and toxicity more accurately in people. They are seen as a new tool for this purpose. These models can be used to provide in vitro methods for predicting effects on the body. A necessary future step is the combination of Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME) processes. Placing these processes within one closed system would meet important needs for pharmaceutical companies. These models have been shown to be effective. They can model important drug bioavailability mechanisms, especially metabolism.
The creation of new pharmaceuticals is an expensive process. It also involves a high risk of failure during tests in humans. Non-human models have been used to understand disease. The use of these models is now a subject of debate. This is partly due to moral concerns. It is also because of the unavoidable pathophysiological differences that exist between animals and humans. Current in vitro models are not able to replace non-human models completely. They do not have sufficient capability or predictivity for human pharmacokinetics and toxicity. New systems are needed to provide better forecasts of human reactions.
These tissue-chip models are believed to be useful for building new tests. Such tests are needed to model and predict important physiological responses. These responses relate to how a medicine is made available in the body. They also relate to its effectiveness and its toxicity. Beyond improving the general efficiency of research, these engineered culture systems may be beneficial in other specific sectors. It is thought they could support and accelerate efforts in rare illnesses. The fields of stratified medicine and nanomedicine may also be helped. These particular areas are currently gaining attention from industry and the public.
A very important step for this technology is combining several processes. The processes of Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME) must be placed within one closed in vitro system. This achievement would meet important pharmaceutical industry needs that are not currently satisfied. The development of these systems is focused on what is needed for industrial use. This means the models must meet specific requirements. These requirements relate to both the structure of the models and their functions. The technology is systemically being presented, from what is already achieved to what still needs to be done.