Introduction
In this paper, Mehnert JM and colleagues discussed the new advances in immuno-oncology and related biomarkers identification challenges. They highlighted that single biomarkers analysis is not informative enough to reflect the complex interaction between the tumor microenvironment and the innate immune system. This is particularly true when addressing the new checkpoint modulator development (eg. PD1/PDL-1 agonist and antagonist). Having access to technologies able to recreate in vitro the complexity of the tumor microenvironment and the patient immune system merged with multiple endpoints analysis seems to be one way to tackle the challenged highlighted by the authors.
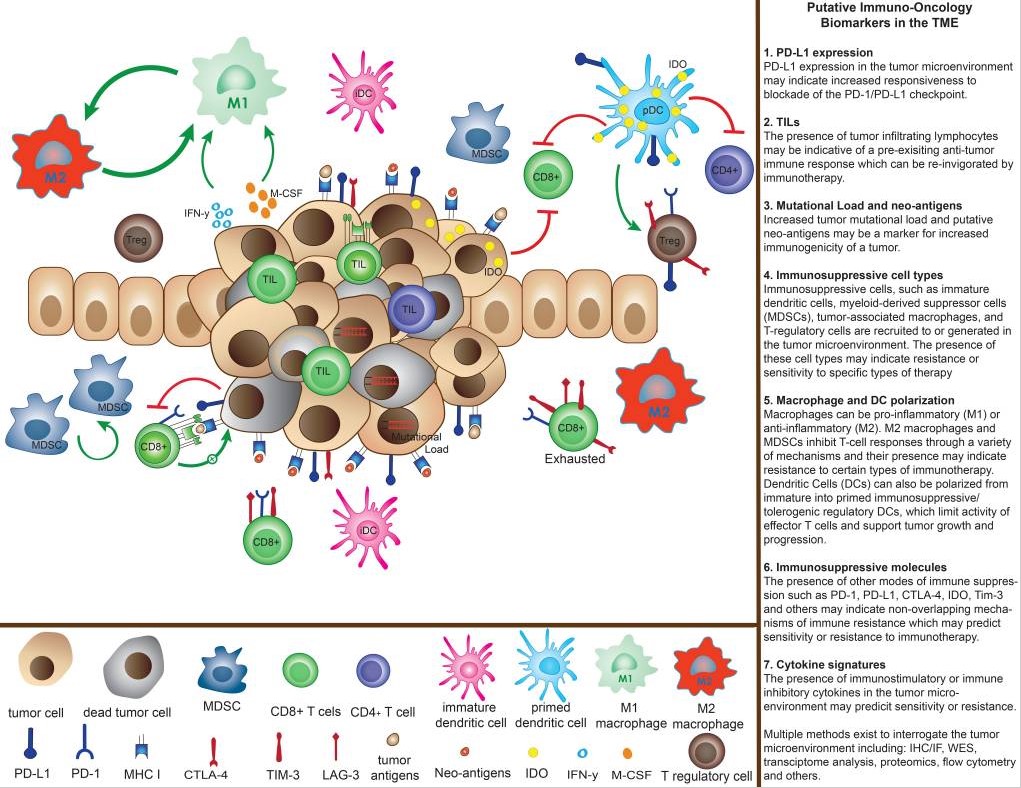
Abstract of The Challenge for Development of Valuable Immuno-Oncology Biomarkers
The development of immunotherapy is an important breakthrough for the treatment of cancer, with antitumor efficacy observed in a wide variety of tumors. To optimize immunotherapy use, approaches must be developed to identify which patients are likely to achieve benefit. To minimize therapeutic toxicities and costs, understanding the ideal choice and sequencing of the numerous immuno-oncology agents available for individual patients is thus critical, but fraught with challenges. The immune tumor microenvironment (TME) is a unique aspect of the response to immuno-oncology agents and measurement of single biomarkers does not adequately capture these complex interactions. Therefore, multiple potential biomarkers are likely needed. Current candidates in this area include PD-L1 expression, CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, tumor mutation load and neoantigen burden, immune-related gene signatures, and multiplex IHC assays that examine the pharmacodynamic and spatial interactions of the TME. The most fruitful investigations are likely to use several techniques to predict response and interrogate mechanisms of resistance. Immuno-oncology biomarker research must employ validated assays to ask focused research questions utilizing clinically annotated tissue collections and biomarker-focused clinical trial designs to investigate specific endpoints. Real-time input from patients and their advocates into biomarker discovery is necessary to ensure that the investigations pursued will improve both clinical outcomes and quality of life. We herein provide a framework of recommendations to guide the search for immuno-oncology biomarkers of value.
References
Mehnert JM, Monjazeb AM, Beerthuijzen JMT, Collyar D, Rubinstein L, Harris LN. The Challenge for Development of Valuable Immuno-oncology Biomarkers. Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 1;23(17):4970-4979. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-3063. PMID: 28864725