Introduction
Biomaterial scaffold like the extracellular matrix (ECM) is the non-cellular component of an organ on chip present within all tissues and organs, which provides not only important physical support in cellular elements but also initiates key biochemicals and biomechanisms for tissue morphogenesis, differentiation, and homeostasis. This review of Biomaterials and Scaffold Fabrication for Organ-on-a-Chip Systems talks about all the requirements for ECM as it will differ in each application.
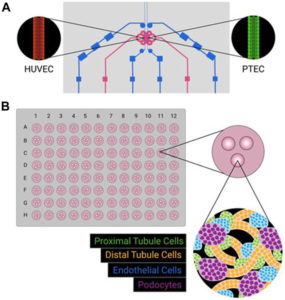
The authors examined the various biomaterials utilized to build scaffolds for Organ on a chip in this publication.
The development of new technology has considerably enhanced Scaffold research and tissue engineering in the last decade. Learn more by reading this review by Osório et al.
How to culture vascularized & immunocompetent 3D models in a standard Multiwell
Abstract of A Review of Biomaterials and Scaffold Fabrication for Organ-on-a-Chip Systems
The authors state that “Drug and chemical development along with safety tests rely on the use of numerous clinical models. This is a lengthy process where animal testing is used as a standard for pre-clinical trials. However, these models often fail to represent human physiopathology.
This may lead to poor correlation with results from later human clinical trials. Organ-on-a-Chip (OOAC) systems are engineered microfluidic systems, which recapitulate the physiochemical environment of a specific organ by emulating the perfusion and shear stress cellular tissue undergoes in vivo and could replace current animal models.
The success of culturing cells and cell-derived tissues within these systems is dependent on the scaffold chosen; hence, scaffolds are critical for the success of OOACs in research.
A literature review was conducted looking at current OOAC systems to assess the advantages and disadvantages of different materials and manufacturing techniques used for scaffold production; and the alternatives that could be tailored from the macro tissue engineering research field.”
References
Osório LA, Silva E, Mackay RE. A Review of Biomaterials and Scaffold Fabrication for Organ-on-a-Chip (OOAC) Systems. Bioengineering (Basel). 2021 Aug 6;8(8):113. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering8080113. PMID: 34436116; PMCID: PMC8389238.
FAQ
A biomaterial scaffold is the non-cellular part found within an organ-on-a-chip system. It is present in all tissues and organs. This component provides physical support to the cellular elements. It also initiates necessary biochemical and biomechanical processes. These processes are required for tissue morphogenesis, which is the shaping of the tissue. They also support differentiation and the maintenance of a stable state, known as homeostasis. The specific requirements for this non-cellular component will differ depending on the application. Researchers have examined various biomaterials that can be used to construct these scaffolds. Progress in technology has allowed for considerable enhancement in scaffold research and the field of tissue engineering.
The development of drugs and chemicals, along with their safety tests, relies on the use of many clinical models. This is a lengthy process. Animal testing is currently used as the standard for pre-clinical trials. A problem exists with these animal models. They often do not correctly represent human physiopathology. This failure to represent human responses may lead to a poor correlation with results from later human clinical trials. Organ-on-a-Chip systems are being developed as an alternative. These systems are engineered to copy the environment of a specific organ. It is thought they could replace the animal models used at present.
Organ-on-a-Chip (OOAC) systems are a type of engineered microfluidic system. Their purpose is to reproduce the physiochemical environment of a specific organ. This is achieved by emulating the perfusion of fluid that tissue experiences. The systems also copy the shear stress that cellular tissue undergoes inside a living body. By recreating these conditions, the OOAC can model the organ’s functions and physical surroundings. These systems are being studied as a potential replacement for current animal models. They are part of an effort to find more representative models for pre-clinical trials that better predict human responses.
The success of culturing cells and tissues within Organ-on-a-Chip systems is connected to the chosen scaffold. Therefore, scaffolds are considered an essential component for the success of these systems in research. A literature review was conducted to assess current OOAC systems. This review examined the benefits and drawbacks of different materials used for scaffold production. It also looked at the various manufacturing techniques. The review further considered alternatives that could be modified from the field of macro tissue engineering. This information helps researchers select the correct scaffold material and production method for their specific application.