Engineered C. elegans as a model organism for a better understanding of type 2 diabetes in humans
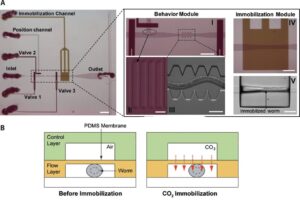
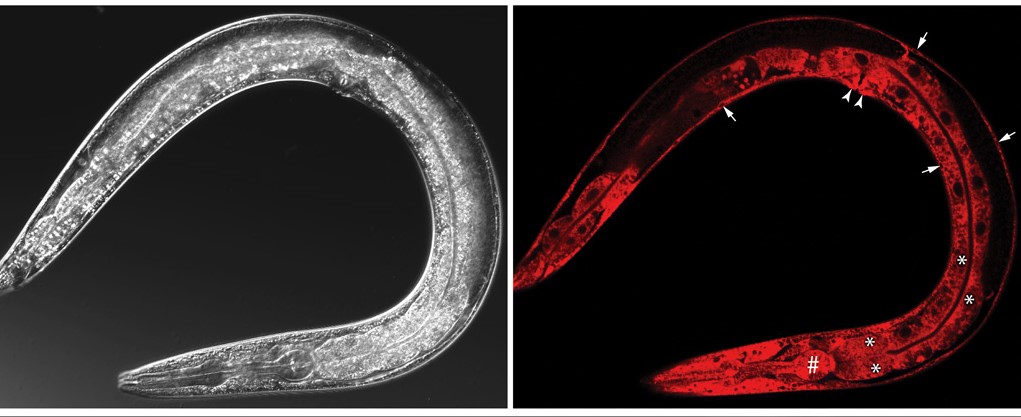
To better understand the mechanisms of peptide hormones, Xin Li et al. performed a research on translocon associated protein α (TRAPα). They reveal a primordial role of TRAPα in the biosynthesis of insulin. They have used C. elegans as a model organism for mammals to better understand the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. The insulin secretion pathway analysis demonstrates the importance of the endoplasmic reticulum translocation machinery in insulin biogenesis. To further extend these findings in rats and humans, they experimented in pancreatic β cells of rats where TRAPα would directly promote preproinsulin translocation, influences proinsulin maturation & insulin secretion. All these advances conduct to suggestions that preproinsulin translocation and proinsulin trafficking could lead to the development of type 2 diabetes.
Ultra fast temperature shift device for in vitro experiments under microscopy
Abstract
“The mechanistic basis for the biogenesis of peptide hormones and growth factors is poorly understood. Here, we show that the conserved endoplasmic reticulum membrane translocon-associated protein α (TRAPα), also known as signal sequence receptor 1, plays a critical role in the biosynthesis of insulin. Genetic analysis in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans and biochemical studies in pancreatic β cells reveal that TRAPα deletion impairs preproinsulin translocation while unexpectedly disrupting distal steps in insulin biogenesis including proinsulin processing and secretion. The association of common intronic single-nucleotide variants in the human TRAPα gene with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes and pancreatic β cell dysfunction suggests that impairment of preproinsulin translocation and proinsulin trafficking may contribute to the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes.”
References
FAQ
Translocon-associated protein ɑ (TRAPɑ) is a conserved protein. It is located in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. It is also referred to as signal sequence receptor 1\. Research has been performed on TRAPɑ to better understand the mechanistic basis for how peptide hormones and growth factors are made. A study used the nematode C. elegans as a model organism for mammals. This research was done to gain a better understanding of the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. The analysis of the insulin secretion pathway shows the importance of the translocation machinery in the endoplasmic reticulum.
A critical function for TRAPɑ in the biosynthesis of insulin has been shown. It is described as having a primordial role in this process. Genetic analysis and biochemical studies revealed that a deletion of TRAPɑ impairs preproinsulin translocation. This was also observed in rat pancreatic ꞵ cells, where TRAPɑ directly promotes this translocation. In addition to this function, the protein was also found to unexpectedly disrupt later steps in insulin biogenesis. These distal steps include the processing of proinsulin and the secretion of insulin.
The role of TRAPɑ was investigated using several methods. A genetic analysis was performed using the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. This organism was used as a model for mammals. The findings were then extended by experimenting in rat pancreatic $\\beta$ cells. Biochemical studies were conducted in these pancreatic ꞵ cells. This was done to confirm the findings in rats and humans. The research was part of an effort to better understand the mechanisms of peptide hormones. It was also aimed at gaining a better understanding of the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes.
A connection has been found between the human TRAPɑ gene and type 2 diabetes. Common single-nucleotide variants, which are found in the introns of the gene, are associated with susceptibility to the disease. These variants are also linked to dysfunction in pancreatic ꞵ cells. These findings lead to a suggestion regarding the development of type 2 diabetes. It is suggested that the pathogenesis of the disease may be contributed to by the impairment of preproinsulin translocation. Issues with the trafficking of proinsulin are also suggested as a factor that could lead to the development of type 2 diabetes.